Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Temporal association between the age-specific incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome and SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in Republic of Korea: a nationwide time-series correlation study
- Hyunju Lee, Donghyok Kwon, Seoncheol Park, Seung Ri Park, Darda Chung, Jongmok Ha
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):224-231. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0050
- 2,086 View
- 89 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 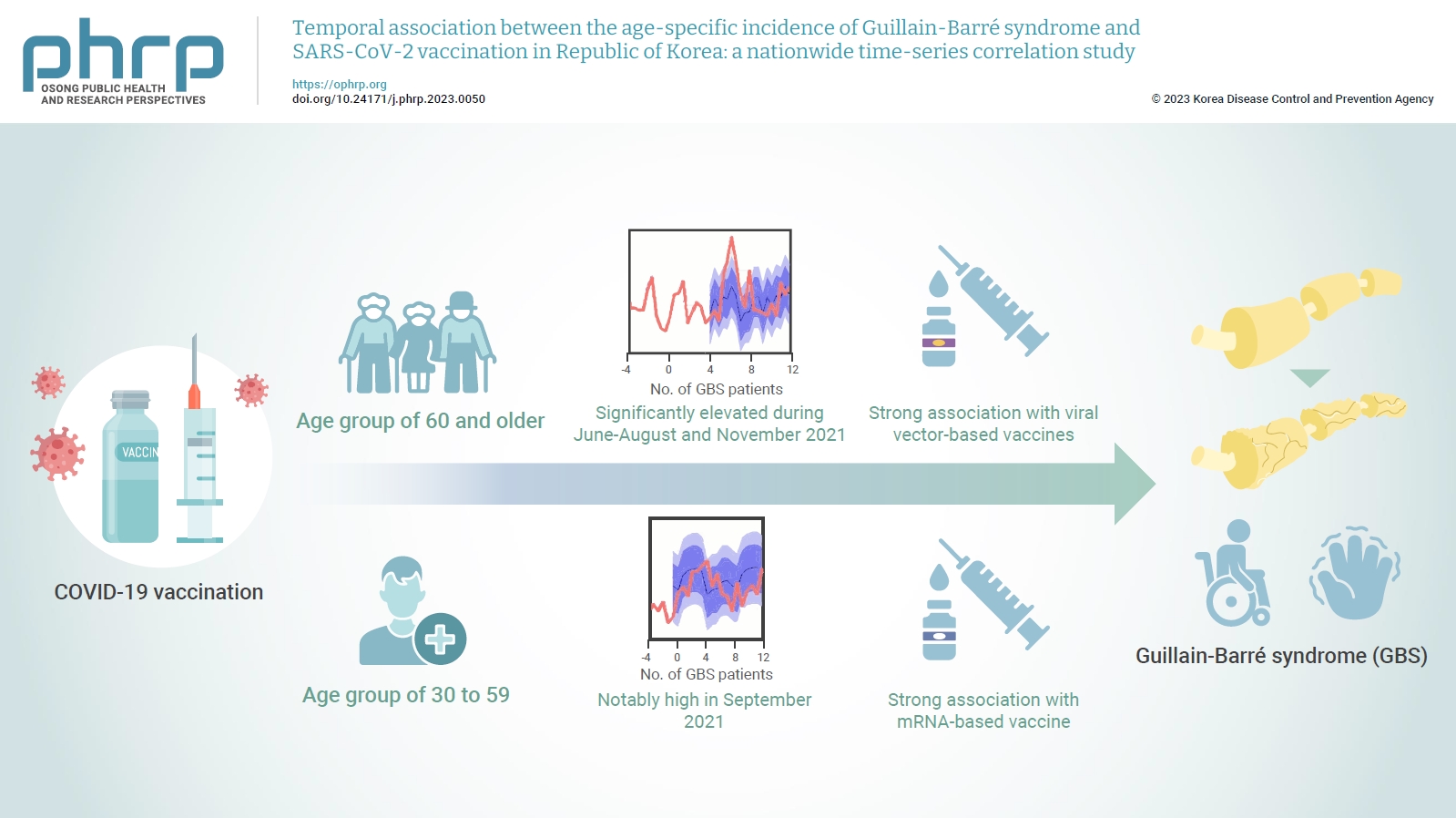
- Objectives
The incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) changed significantly during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Emerging reports suggest that viral vector-based vaccines may be associated with an elevated risk of GBS.
Methods
In this nationwide time-series correlation study, we examined the age-specific incidence of GBS from January 2011 to August 2022, as well as data on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccinations and infections from February 2021 to August 2022. We compared the forecasted estimates of age-specific GBS incidence, using the pre-SARS-CoV-2 period as a benchmark, with the actual incidence observed during the post-vaccination period of the pandemic. Furthermore, we assessed the temporal association between GBS, SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations, and COVID-19 for different age groups.
Results
In the age group of 60 and older, the rate ratio was significantly elevated during June-August and November 2021. A significant, strong positive association was observed between viral vector-based vaccines and GBS incidence trends in this age group (r=0.52, p=0.022). For the 30 to 59 years age group, the rate ratio was notably high in September 2021. A statistically significant, strong positive association was found between mRNA-based vaccines and GBS incidence in this age group (r=0.61, p=0.006).
Conclusion
Viral vector-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines were found to be temporally associated with an increased risk of GBS, particularly in older adults. To minimize age-specific and biological mechanism-specific adverse events, future vaccination campaigns should adopt a more personalized approach, such as recommending homologous mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for older adults to reduce the heightened risk of GBS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- mRNA-LNP COVID-19 Vaccine Lipids Induce Complement Activation and Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines: Mechanisms, Effects of Complement Inhibitors, and Relevance to Adverse Reactions
Tamás Bakos, Tamás Mészáros, Gergely Tibor Kozma, Petra Berényi, Réka Facskó, Henriette Farkas, László Dézsi, Carlo Heirman, Stefaan de Koker, Raymond Schiffelers, Kathryn Anne Glatter, Tamás Radovits, Gábor Szénási, János Szebeni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3595. CrossRef - Guillain–Barre syndrome following COVID-19 vaccination: a study of 70 case reports
Biki Kumar Sah, Zahra Fatima, Rajan Kumar Sah, Bushra Syed, Tulika Garg, Selia Chowdhury, Bikona Ghosh, Binita Kunwar, Anagha Shree, Vivek Kumar Sah, Anisha Raut
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2024; 86(4): 2067. CrossRef
- mRNA-LNP COVID-19 Vaccine Lipids Induce Complement Activation and Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines: Mechanisms, Effects of Complement Inhibitors, and Relevance to Adverse Reactions
- Vaccine effectiveness and the epidemiological characteristics of a COVID-19 outbreak in a tertiary hospital in Republic of Korea
- Seonhee Ahn, Tae Jong Son, Yoonsuk Jang, Jihyun Choi, Young Joon Park, Jiseon Seong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Muk Ju Kim, Donghyok Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):188-196. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0066
- 1,462 View
- 72 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 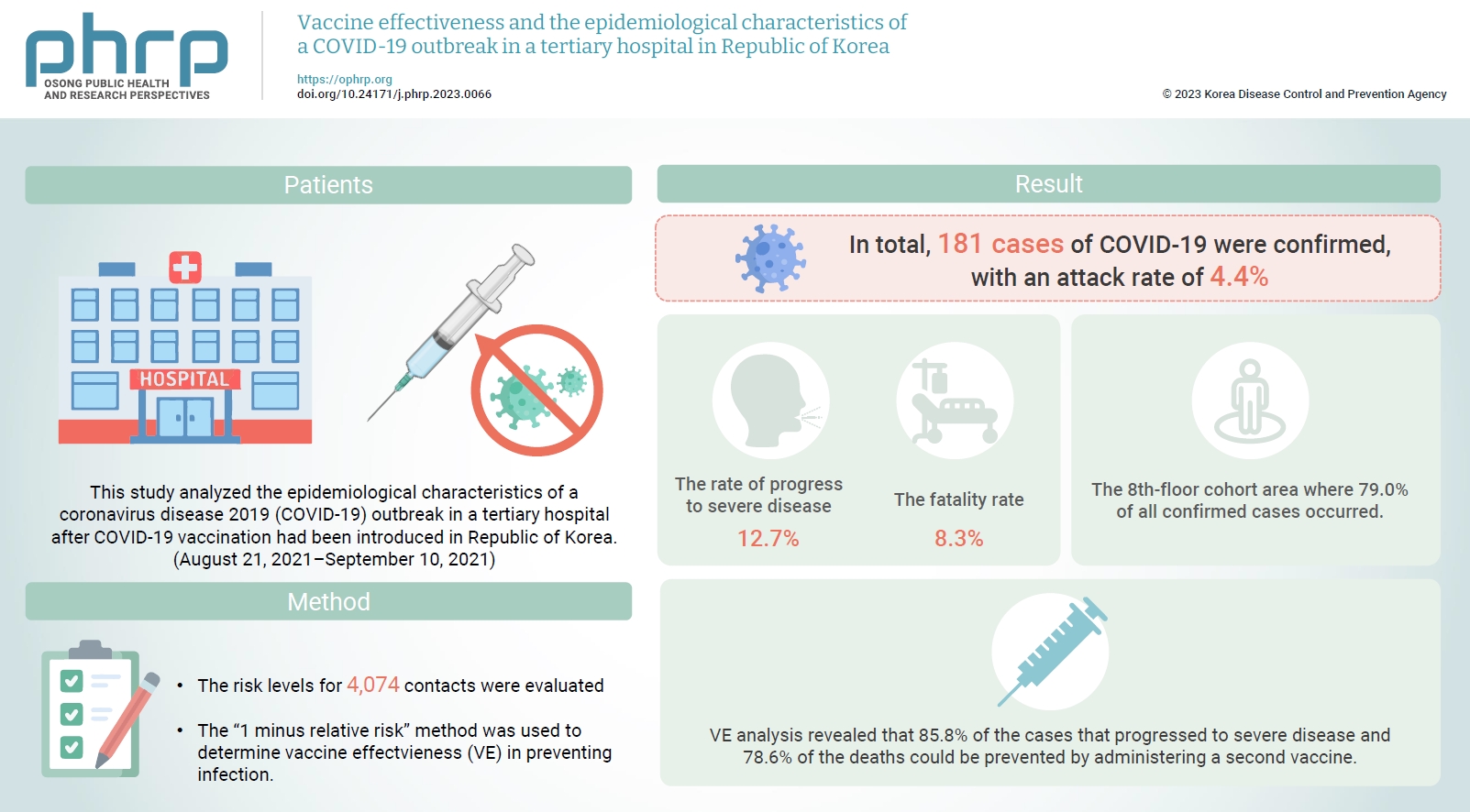
- Objectives
Healthcare facilities are high-risk sites for infection. This study analyzed the epidemiological characteristics of a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in a tertiary hospital after COVID-19 vaccination had been introduced in Republic of Korea. Vaccine effectiveness (VE) and shared anti-infection strategies are also assessed.
Methods
The risk levels for 4,074 contacts were evaluated. The epidemiological characteristics of confirmed cases were evaluated using the chi-square test. The “1 minus relative risk” method was used to determine VE in preventing infection, progression to severe disease, and death. In the largest affected area (the 8th floor), a separate relative risk analysis was conducted. A multivariate logistic regression analysis (with 95% confidence interval [CIs]) was used to identify transmission risk factors with a significance level <10% via the backward elimination method.
Results
In total, 181 cases of COVID-19 were confirmed, with an attack rate of 4.4%. Of those cases, 12.7% progressed to severe disease, and 8.3% died. In the cohort isolation area on the 8th floor, where 79.0% of the confirmed cases occurred, the adjusted odds ratio was 6.55 (95% CI, 2.99–14.33) and 2.19 (95% CI, 1.24–3.88) for caregivers and the unvaccinated group, respectively. VE analysis revealed that 85.8% of the cases that progressed to severe disease and 78.6% of the deaths could be prevented by administering a second vaccine.
Conclusion
Caregiver training for infection prevention and control is necessary to reduce infection risk. Vaccination is an important intervention to reduce the risk of progression to severe disease and death.
- Risk factors for deaths associated with COVID-19 according to the cause of death classification in Republic of Korea
- Na-Young Kim, Seong-Sun Kim, Hyun Ju Lee, Dong Hwi Kim, Boyeong Ryu, Eunjeong Shin, Donghyok Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):89-99. Published online April 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0312
- 1,452 View
- 93 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
This study aimed to classify coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-related deaths according to whether COVID-19 was listed as the cause of death, and to investigate the differences in demographic characteristics and risk factors for COVID-19 death classifications.
Methods
A total of 5,625 deaths in South Korea among patients with confirmed COVID-19 from January 20, 2020 to December 31, 2021 were selected. Excluding false reports and unnatural deaths, 5,597 deaths were analyzed. Based on death report data, deaths were classified according to whether the cause of death was listed as COVID-19 (CD) or not (NCD). The epidemiological characteristics and causes of deaths were investigated using descriptive, univariate, and multivariate statistical analyses. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to analyze the risk factors.
Results
The case fatality ratio was 0.89% and increased with age. Additionally, 96.4% of the subjects had an underlying disease, and 53.4% died in winter. The proportion of NCDs was 9.3%, of whom 19.1% died at home and 39.0% were confirmed to have COVID-19 after death. Malignant neoplasms (102/416 vs. 637/4,442; OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.36−2.16; p<0.001) were significantly associated with NCD.
Conclusion
This is the first study to analyze risk factors by cause of death using COVID-19 death report data in South Korea. These results are expected to be used as evidence for establishing a death monitoring system that can collect timely information in a new infectious disease pandemic.
- Review of the early reports of the epidemiological characteristics of the B.1.1.7 variant of SARS-CoV-2 and its spread worldwide
- Yeonju Kim, Eun-Jin Kim, Sang-Won Lee, Donghyok Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(3):139-148. Published online June 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0037
- 6,483 View
- 151 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The variant B.1.1.7 of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the RNA virus causing the pandemic more than a year worldwide, was reported from United Kingdom (UK) in late December 2020. It was reported that mortality increases by 65% and transmissibility increases by 70%, which may result in an increase of reproduction number to 1.13−1.55 from 0.75−0.85. To analyze the global increasing trend of the variant B.1.1.7, we extracted results of B.1.1.7 from GISAID on May 11 and May 12, 2021, and conducted a doseresponse regression. It took 47 days to reach 20% and 121 days to reach 50% among the sequence submitted from UK. In Korea, cases of B.1.1.7 have increased since the first report of three cases on December 28, 2020. Positive rate of B.1.1.7 in Korea was 21.6% in the week from May 9 to May 15, 2021. Detection rate of the variants is expected to increase further and new variants of SARS-CoV-2 are emerging, so a close monitoring and control would be maintained for months.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mutations in SARS-CoV-2: Insights on structure, variants, vaccines, and biomedical interventions
Ahmed I. Abulsoud, Hussein M. El-Husseiny, Ahmed A. El-Husseiny, Hesham A. El-Mahdy, Ahmed Ismail, Samy Y. Elkhawaga, Emad Gamil Khidr, Doaa Fathi, Eman A. Mady, Agnieszka Najda, Mohammad Algahtani, Abdulrahman Theyab, Khalaf F. Alsharif, Ashraf Albrakati
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 157: 113977. CrossRef - Structural implications of SARS-CoV-2 Surface Glycoprotein N501Y mutation within receptor-binding domain [499-505] – computational analysis of the most frequent Asn501 polar uncharged amino acid mutations
Done Stojanov
Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular and Clinical Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Individuals in a Large Healthcare Organization from New Jersey
José R. Mediavilla, Tara Lozy, Annie Lee, Justine Kim, Veronica W. Kan, Elizabeth Titova, Ashish Amin, Michael C. Zody, André Corvelo, Dayna M. Oschwald, Amy Baldwin, Samantha Fennessey, Jerry M. Zuckerman, Thomas Kirn, Liang Chen, Yanan Zhao, Kar Fai Cho
Viruses.2023; 15(8): 1699. CrossRef - Incidence Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in the Ulsan Area, Korea, Using PowerChek SARS-CoV-2 S-gene Mutation Detection Kit: A Pilot Study
Sang Hyuk Park, Hyun-Ki Kim, Hang Kang, Jung Heon Kim, Jaeseung Lee, Ji-Hun Lim, Seon-Ho Lee, Joseph Jeong
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2022; 42(3): 363. CrossRef - Biological Properties of SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Epidemiological Impact and Clinical Consequences
Reem Hoteit, Hadi M. Yassine
Vaccines.2022; 10(6): 919. CrossRef - Virtual recruitment and participant engagement for substance use research during a pandemic
Carolin C. Hoeflich, Anna Wang, Ayodeji Otufowora, Linda B. Cottler, Catherine W. Striley
Current Opinion in Psychiatry.2022; 35(4): 252. CrossRef - Display of receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein variants on the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell surface
Hongguan Xing, Liyan Zhu, Pingping Wang, Guoping Zhao, Zhihua Zhou, Yi Yang, Hong Zou, Xing Yan
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid in variants of concern impair the sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 detection by rapid antigen tests
Ibrahim T. Hagag, Krzysztof Pyrc, Saskia Weber, Anne Balkema-Buschmann, Martin H. Groschup, Markus Keller
Frontiers in Virology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes of the SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern
Lixin Lin, Ying Liu, Xiujuan Tang, Daihai He
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mutations in SARS-CoV-2: Insights on structure, variants, vaccines, and biomedical interventions
- Genomic Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2: Distribution of Clades in the Republic of Korea in 2020
- Ae Kyung Park, Il-Hwan Kim, Junyoung Kim, Jeong-Min Kim, Heui Man Kim, Chae young Lee, Myung-Guk Han, Gi-Eun Rhie, Donghyok Kwon, Jeong-Gu Nam, Young-Joon Park, Jin Gwack, Nam-Joo Lee, SangHee Woo, Jin Sun No, Jaehee Lee, Jeemin Ha, JeeEun Rhee, Cheon-Kwon Yoo, Eun-Jin Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(1):37-43. Published online February 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.12.1.06
- 9,172 View
- 223 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Since a novel beta-coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was first reported in December 2019, there has been a rapid global spread of the virus. Genomic surveillance was conducted on samples isolated from infected individuals to monitor the spread of genetic variants of SARS-CoV-2 in Korea. The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency performed whole genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 in Korea for 1 year (January 2020 to January 2021). A total of 2,488 SARS-CoV-2 cases were sequenced (including 648 cases from abroad). Initially, the prevalent clades of SARS-CoV-2 were the S and V clades, however, by March 2020, GH clade was the most dominant. Only international travelers were identified as having G or GR clades, and since the first variant 501Y.V1 was identified (from a traveler from the United Kingdom on December 22nd, 2020), a total of 27 variants of 501Y.V1, 501Y.V2, and 484K.V2 have been classified (as of January 25th, 2021). The results in this study indicated that quarantining of travelers entering Korea successfully prevented dissemination of the SARS-CoV-2 variants in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased viral load in patients infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron variant in the Republic of Korea
Jeong-Min Kim, Dongju Kim, Nam-Joo Lee, Sang Hee Woo, Jaehee Lee, Hyeokjin Lee, Ae Kyung Park, Jeong-Ah Kim, Chae Young Lee, Il-Hwan Kim, Cheon Kwon Yoo, Eun-Jin Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(4): 272. CrossRef - Rapid Emergence of the Omicron Variant of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Korea
Ae Kyung Park, Il-Hwan Kim, Chae Young Lee, Jeong-Ah Kim, Hyeokjin Lee, Heui Man Kim, Nam-Joo Lee, SangHee Woo, Jaehee Lee, JeeEun Rhee, Cheon-Kwon Yoo, Eun-Jin Kim
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2023; 43(2): 211. CrossRef - A Seroprevalence Study on Residents in a Senior Care Facility with Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Infection
Heui Man Kim, Eun Ju Lee, Sang Won O, Yong Jun Choi, Hyeokjin Lee, Sae Jin Oh, Jeong-Min Kim, Ae Kyung Park, Jeong-Ah Kim, Chae young Lee, Jong Mu Kim, Hanul Park, Young Joon Park, Jeong-Hee Yu, Eun-Young Kim, Hwa-Pyeong Ko, Eun-Jin Kim
Viral Immunology.2023; 36(3): 203. CrossRef - COVID-19 Cases and Deaths among Healthcare Personnel with the Progression of the Pandemic in Korea from March 2020 to February 2022
Yeonju Kim, Sung-Chan Yang, Jinhwa Jang, Shin Young Park, Seong Sun Kim, Chansoo Kim, Donghyok Kwon, Sang-Won Lee
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease.2023; 8(6): 308. CrossRef - The COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare utilization in Iran: evidence from an interrupted time series analysis
Monireh Mahmoodpour-Azari, Satar Rezaei, Nasim Badiee, Mohammad Hajizadeh, Ali Mohammadi, Ali Kazemi-Karyani, Shahin Soltani, Mehdi Khezeli
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(3): 180. CrossRef - Online Phylogenetics with matOptimize Produces Equivalent Trees and is Dramatically More Efficient for Large SARS-CoV-2 Phylogenies than de novo and Maximum-Likelihood Implementations
Alexander M Kramer, Bryan Thornlow, Cheng Ye, Nicola De Maio, Jakob McBroome, Angie S Hinrichs, Robert Lanfear, Yatish Turakhia, Russell Corbett-Detig, Olivier Gascuel
Systematic Biology.2023; 72(5): 1039. CrossRef - Genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 variants in South Korea between January 2020 and February 2023
Il-Hwan Kim, Jin Sun No, Jeong-Ah Kim, Ae Kyung Park, HyeokJin Lee, Jeong-Min Kim, Nam-Joo Lee, Chi-Kyeong Kim, Chae Young Lee, SangHee Woo, Jaehee Lee, JeeEun Rhee, Eun-Jin Kim
Virology.2023; 587: 109869. CrossRef - Genomic evidence of SARS‐CoV‐2 reinfection in the Republic of Korea
Ae Kyung Park, Jee Eun Rhee, Il‐Hwan Kim, Heui Man Kim, Hyeokjin Lee, Jeong‐Ah Kim, Chae Young Lee, Nam‐Joo Lee, SangHee Woo, Jaehee Lee, Jin Sun No, Gi‐Eun Rhie, Seong Jin Wang, Sang‐Eun Lee, Young Joon Park, Gemma Park, Jung Yeon Kim, Jin Gwack, Cheon‐K
Journal of Medical Virology.2022; 94(4): 1717. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 B.1.619 and B.1.620 Lineages, South Korea, 2021
Ae Kyung Park, Il-Hwan Kim, Heui Man Kim, Hyeokjin Lee, Nam-Joo Lee, Jeong-Ah Kim, SangHee Woo, Chae young Lee, Jaehee Lee, Sae Jin Oh, JeeEun Rhee, Cheon-Kwon Yoo, Eun-Jin Kim
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2022; 28(2): 415. CrossRef - Humoral and Cellular Responses to COVID-19 Vaccines in SARS-CoV-2 Infection-Naïve and -Recovered Korean Individuals
Ji-Young Hwang, Yunhwa Kim, Kyung-Min Lee, Eun-Jeong Jang, Chang-Hoon Woo, Chang-Ui Hong, Seok-Tae Choi, Sivilay Xayaheuang, Jong-Geol Jang, June-Hong Ahn, Hosun Park
Vaccines.2022; 10(2): 332. CrossRef - Increase in Viral Load in Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant Infection in the Republic of Korea
Jeong-Min Kim, Jee Eun Rhee, Myeongsu Yoo, Heui Man Kim, Nam-Joo Lee, Sang Hee Woo, Hye-Jun Jo, Donghyok Kwon, Sangwon Lee, Cheon Kwon Yoo, Eun-Jin Kim
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Dynamics Studies on the Structural Stability Prediction of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Including Multiple Mutants
Kwang-Eun Choi, Jeong-Min Kim, Jee Eun Rhee, Ae Kyung Park, Eun-Jin Kim, Cheon Kwon Yoo, Nam Sook Kang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(9): 4956. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 shedding dynamics and transmission in immunosuppressed patients
Jee-Soo Lee, Ki Wook Yun, Hyeonju Jeong, Boram Kim, Man Jin Kim, Jae Hyeon Park, Ho Seob Shin, Hyeon Sae Oh, Hobin Sung, Myung Gi Song, Sung Im Cho, So Yeon Kim, Chang Kyung Kang, Pyoeng Gyun Choe, Wan Beom Park, Nam Joong Kim, Myoung-Don Oh, Eun Hwa Choi
Virulence.2022; 13(1): 1242. CrossRef - Immunological and Pathological Peculiarity of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Beta Variant
Sunhee Lee, Gun Young Yoon, Su Jin Lee, Young-Chan Kwon, Hyun Woo Moon, Yu-Jin Kim, Haesoo Kim, Wooseong Lee, Gi Uk Jeong, Chonsaeng Kim, Kyun-Do Kim, Seong-Jun Kim, Dae-Gyun Ahn, Miguel Angel Martinez
Microbiology Spectrum.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical scoring system to predict viable viral shedding in patients with COVID-19
Sung Woon Kang, Heedo Park, Ji Yeun Kim, Sunghee Park, So Yun Lim, Sohyun Lee, Joon-Yong Bae, Jeonghun Kim, Seongman Bae, Jiwon Jung, Min Jae Kim, Yong Pil Chong, Sang-Oh Lee, Sang-Ho Choi, Yang Soo Kim, Sung-Cheol Yun, Man-Seong Park, Sung-Han Kim
Journal of Clinical Virology.2022; 157: 105319. CrossRef - Model-informed COVID-19 exit strategy with projections of SARS-CoV-2 infections generated by variants in the Republic of Korea
Sung-mok Jung, Kyungmin Huh, Munkhzul Radnaabaatar, Jaehun Jung
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative analysis of mutational hotspots in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 isolates from different geographic origins
Sanghoo Lee, Mi-Kyeong Lee, Hyeongkyun Na, Jinwoo Ahn, Gayeon Hong, Youngkee Lee, Jimyeong Park, Yejin Kim, Yun-Tae Kim, Chang-Ki Kim, Hwan-Sub Lim, Kyoung-Ryul Lee
Gene Reports.2021; 23: 101100. CrossRef - Review of Current COVID-19 Diagnostics and Opportunities for Further Development
Yan Mardian, Herman Kosasih, Muhammad Karyana, Aaron Neal, Chuen-Yen Lau
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Locally harvested Covid-19 convalescent plasma could probably help combat the geographically determined SARS-CoV-2 viral variants
Manish Raturi, Anuradha Kusum, Mansi Kala, Garima Mittal, Anita Sharma, Naveen Bansal
Transfusion Clinique et Biologique.2021; 28(3): 300. CrossRef - Molecular Dynamics Studies on the Structural Characteristics for the Stability Prediction of SARS-CoV-2
Kwang-Eun Choi, Jeong-Min Kim, JeeEun Rhee, Ae Kyung Park, Eun-Jin Kim, Nam Sook Kang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(16): 8714. CrossRef - Management following the first confirmed case of SARS-CoV-2 in a domestic cat associated with a massive outbreak in South Korea
Taewon Han, Boyeong Ryu, Suyeon Lee, Yugyeong Song, Yoongje Jeong, Ilhwan Kim, Jeongmin Kim, Eunjin Kim, Wonjun Lee, Hyunju Lee, Haekyoung Hwang
One Health.2021; 13: 100328. CrossRef - Genomic epidemiology reveals the reduction of the introduction and spread of SARS-CoV-2 after implementing control strategies in Republic of Korea, 2020
Jung-Hoon Kwon, Jeong-Min Kim, Dong-hun Lee, Ae Kyung Park, Il-Hwan Kim, Da-Won Kim, Ji-Yun Kim, Noori Lim, Kyeong-Yeon Cho, Heui Man Kim, Nam-Joo Lee, SangHee Woo, Chae Young Lee, Jin Sun No, Junyoung Kim, JeeEun Rhee, Myung-Guk Han, Gi-Eun Rhie, Cheon K
Virus Evolution.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Increased viral load in patients infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron variant in the Republic of Korea
- Imported Melioidosis in South Korea: A Case Series with a Literature Review
- Seung Woo Kim, Geun-Yong Kwon, Bongyoung Kim, Donghyok Kwon, Jaeseung Shin, Geun-Ryang Bae
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(6):363-368. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.10.014
- 2,846 View
- 18 Download
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Melioidosis is a potentially fatal infectious disease caused by the environmental anaerobic Gram-negative bacillus Burkholderia pseudomallei. Melioidosis is endemic to areas of northern Australia and Southeast Asia. With increasing international travel and migration, imported cases of melioidosis are being reported regularly. Here, we summarize the 11 cases of melioidosis reported in South Korea from 2003 to 2014.
Methods
Tracing epidemiological investigations were performed on every patient reported to the National Surveillance System since 2011. A systematic literature search was performed to identify melioidosis cases that occurred prior to 2011.
Results
The overall fatality rate was 36.4%. All the patients had visited Southeast Asia where melioidosis is endemic. The stay in the endemic region ranged from 4 days to 20 years. Of the seven patients who developed initial symptoms after returning to South Korea, the time interval between returning to South Korea and symptom onset ranged from 1 day to 3 years. The remaining four patients developed symptoms during their stay in the endemic region and were diagnosed with melioidosis in South Korea. Seven (63.6%) patients possessed at least one risk factor, all of whom were diabetic. Pneumonia was the most frequent clinical manifestation, but the patients showed a wide spectrum of clinical features, including internal organ abscesses, a mycotic aneurysm of the aorta, and coinfection with tuberculosis.
Conclusion
An early diagnosis and initiation of the appropriate antibiotics can reduce the mortality of melioidosis. Consequently, increased awareness of the risk factors and clinical features of melioidosis is required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An overview of the study designs and statistical methods used in the determination of predictors of melioidosis mortality in Malaysia: 2010-2021
Kamaruddin Mardhiah, Othman Nursyahiyatul-Anis
Pedagogical Research.2024; 9(3): em0205. CrossRef - Epidemiological Aspects of Imported Melioidosis in Korea and Japan, 2011 to 2020
Myeong-Jin Lee, Kyu Sung Kim, Won-Chang Lee, Young Hwan Kwon
The Korean Journal of Aerospace and Environmental .2023; 33(1): 32. CrossRef - The Cox model of predicting mortality among melioidosis patients in Northern Malaysia
Kamaruddin Mardhiah, Nadiah Wan-Arfah, Nyi Nyi Naing, Muhammad Radzi Abu Hassan, Huan-Keat Chan
Medicine.2021; 100(25): e26160. CrossRef - Tuberculosis and Melioidosis at Distinct Sites Occurring Simultaneously
Seow Yen Tan
Case Reports in Infectious Diseases.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef -
Burkholderia pseudomallei pathogenesis and survival in different niches
Chee-Hoo Yip, Ahmad-Kamal Ghazali, Sheila Nathan
Biochemical Society Transactions.2020; 48(2): 569. CrossRef - Mycotic aneurysm secondary to melioidosis in China: A series of eight cases and a review of literature
Hua Wu, Xuming Wang, Xiaojun Zhou, Zhicheng Wu, Yanyan Wang, Mengjie Pan, Binghuai Lu, Susanna Jane Dunachie
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.2020; 14(8): e0008525. CrossRef - Fatal deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism secondary to melioidosis in China: case report and literature review
Hua Wu, Dongliang Huang, Biao Wu, Mengjie Pan, Binghuai Lu
BMC Infectious Diseases.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Melioidosis in the Philippines
Peter San Martin, Joseph Chua, Ralph Bautista, Jennifer Nailes, Mario Panaligan, David Dance
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease.2018; 3(3): 99. CrossRef - Clinical and Imaging Findings of Musculoskeletal Melioidosis in the Right Hip: A Case Report
Myung Hyun Kim, Tong Jin Chun
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2018; 78(3): 212. CrossRef - Draft Genome Sequence of the First South Korean Clinical Isolate of Burkholderia pseudomallei, H0901
Yong-Woo Shin, Myung-Min Choi, Jeong-Hoon Chun, Jae-Yon Yu, Dae-Won Kim, Gi-eun Rhie
Genome Announcements.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Accidental Occupational Exposure to Burkholderia pseudomallei in South Korea Did Not Result in Melioidosis
Jae-Bum Jun, Taehoon Lee, Joseph Jeong, Jeong-Hoon Chun, Yong-Woo Shin, Jiwon Jung
Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.2017; 38(7): 886. CrossRef - Molecular detection of leptospirosis and melioidosis co-infection: A case report
Mohammad R. Mohd Ali, Amira W. Mohamad Safiee, Padmaloseni Thangarajah, Mohd H. Fauzi, Alwi Muhd Besari, Nabilah Ismail, Chan Yean Yean
Journal of Infection and Public Health.2017; 10(6): 894. CrossRef
- An overview of the study designs and statistical methods used in the determination of predictors of melioidosis mortality in Malaysia: 2010-2021
- Development of a Specific and Rapid Diagnostic Method for Detecting Influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 Virus Infection Using Immunochromatographic Assay
- Mi Jung Ji, Byung Ki Cho, Young Shik Cho, Young Jin Choi, Donghyok Kwon, Kyeongcheol Shin, Joo-Yeon Lee, Chun Kang, Byoung Su Yoon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(6):342-346. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.10.006
- 2,963 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to develop an immunochromatographic assay (ICA) for the detection of influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 virus infection. Materials and methods Several monoclonal antibodies against influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 virus were generated and an ICA (pdm09-ICA) was developed for the rapid and specific detection of influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 virus infection. The specificity and sensitivity of the developed assay were compared with that of hemagglutination assay and real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR).
Results
The detection limit was estimated to be 1/2 (8) hemagglutinating unit; the sensitivity and specificity rates of pdm09-ICA were 75.86% (110/145) and 100% (43/43), respectively, compared with rRT-PCR. The cross-reactivity for 20 influenza viruses, including seasonal H1N1 viruses, was found to be negative except for the H1N1 virus (A/Swine/Korea/GC0503/2005).
Conclusion
These results indicate that the proposed method can be easily used for rapid and specific detection of the pdm09 infection. The assay developed in this study would be a useful tool for distinguishing the pdm09 infection from seasonal influenza A and B infections. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sensitive detection of influenza a virus based on a CdSe/CdS/ZnS quantum dot-linked rapid fluorescent immunochromatographic test
Anh Viet Thi Nguyen, Tung Duy Dao, Tien Thi Thuy Trinh, Du-Young Choi, Seung-Taek Yu, Hyun Park, Seon-Ju Yeo
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2020; 155: 112090. CrossRef - Detecting Influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 Virus Infection Using Immunochromatographic Assay
Viroj Wiwanitkit
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2014; 5(2): 115. CrossRef
- Sensitive detection of influenza a virus based on a CdSe/CdS/ZnS quantum dot-linked rapid fluorescent immunochromatographic test
- Pathogenesis and Chronologic Localization of the Human Influenza A (H1N1) Virus in Cotton Rats
- Donghyok Kwon, Kyeongcheol Shin, Jin-Young Shin, Joo-Yeon Lee, Yooncheol Ha, Nam-Joo Lee, Hee-Bok Oh, Chanhee Chae, Chun Kang
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2011;2(1):15-22. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2011.04.005
- 2,950 View
- 24 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We aimed to evaluate the pathogenesis and chronologic localization of human influenza A (H1N1) virus in experimentally infected cotton rats.
Methods
The animals were intranasally inoculated with 107 plaque-forming units of A/Solomon Islands/3/2006 (H1N1) influenza virus and evaluated for pathogenicity for a period of 28 days. Virus replication kinetics and pathological properties were assessed chronologically. Acute antiviral responses were evaluated by mean of real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results
Cotton rats infected with A/Solomon Islands/3/2006 virus lost weight until 6 days post-inoculation (DPI) and showed decreased activity until 3 DPI. At necropsy, focal areas of redness and consolidation of lungs were evident at 1, 2, and 3 DPI. Lung histopathology showed moderate to severe interstitial pneumonia, alveolitis and bronchiolitis. Influenza A specific viral protein was detected in bronchiolar epithelial cells, alveolar septa and pneumocytes. Influenza viruses were recovered from the lungs during the early period of infection and the titer peaked at 1 DPI. Viral proteins were detected from 4 hours to 6 hours DPI. These trends correlate with the up-regulation of mRNA expression of the IFN-α, Mx1, and Mx2 genes that play critical roles in the anti-influenza response at the early stage of infection.
Conclusion
Our results provide evidence that supports the use of cotton rats for the study of influenza virus pathogenesis and the immune response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterization of humoral immune responses and degree of protection induced by influenza vaccine in cotton rats: Effects of low vaccine dose and single vs booster vaccination
Yoshita Bhide, Wei Dong, Tjarko Meijerhof, Jacqueline de Vries‐Idema, Hubert G. Niesters, Anke Huckriede
Immunity, Inflammation and Disease.2020; 8(3): 279. CrossRef - Doing Mathematics with Aftermath of Pandemic Influenza 2009
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2015; 6(1): 1. CrossRef - Assessment of Intensive Vaccination and Antiviral Treatment in 2009 Influenza Pandemic in Korea
Chaeshin Chu, Sunmi Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2015; 6(1): 47. CrossRef - Mammalian pathogenesis of oseltamivir-resistant pandemic (H1N1) 2009 influenza virus isolated in South Korea
Donghyok Kwon, Kyeongcheol Shin, Su-Jin Kim, Joo-Yeon Lee, Chun Kang
Virus Research.2014; 185: 41. CrossRef - Was the Mass Vaccination Effective During the Influenza Pandemic 2009–2010 in Korea?
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2013; 4(4): 177. CrossRef - How to Manage a Public Health Crisis and Bioterrorism in Korea
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2013; 4(5): 223. CrossRef - The Road Less Traveled
Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2011; 2(1): 1. CrossRef
- Characterization of humoral immune responses and degree of protection induced by influenza vaccine in cotton rats: Effects of low vaccine dose and single vs booster vaccination



 First
First Prev
Prev


